It is a condition that affects approximately 3-20% of pregnant women in Canada and can have serious health consequences for both the mother and the baby if not properly managed. In this blog, we will discuss what gestational diabetes is, its causes, risk factors, symptoms, diagnosis, and management in Canada.
What is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy and usually goes away after delivery. It occurs when the body is unable to produce enough insulin or use it effectively, resulting in high blood sugar levels. Insulin is a hormone produced by the pancreas that helps regulate blood sugar levels in the body. During pregnancy, the placenta produces hormones that can make it harder for the body to use insulin effectively, leading to gestational diabetes.
Causes of Gestational Diabetes
The exact cause of gestational diabetes is not known, but it is believed to be related to hormonal changes during pregnancy. The placenta produces hormones that can make it harder for the body to use insulin effectively, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Risk Factors for Gestational Diabetes
Several risk factors can increase a woman’s chances of developing gestational diabetes, including:
- Being overweight or obese
- Having a family history of diabetes
- Having previously given birth to a baby weighing more than 9 pounds
- Being over the age of 35
- Having polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- Having a history of gestational diabetes in a previous pregnancy
- Being of certain ethnicities, such as Indigenous, South Asian, African, or Hispanic descent
Symptoms of Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes often does not cause any symptoms, which is why pregnant women need to be screened for it. However, some women may experience symptoms such as:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Nausea and vomiting
Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes
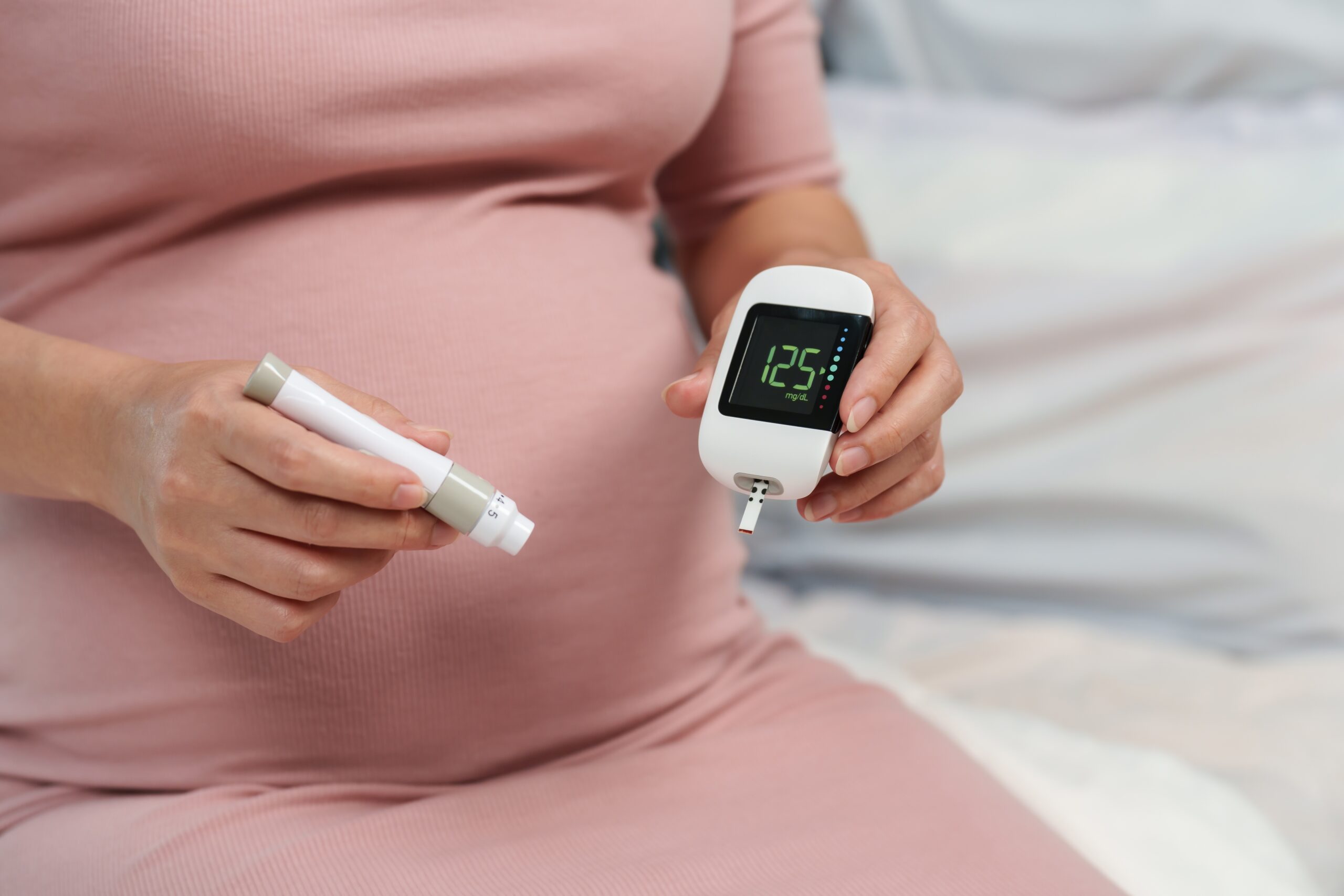
All pregnant women in Canada are screened for gestational diabetes between 24 and 28 weeks of pregnancy. The screening test involves drinking a sugary drink and having blood drawn one hour later to measure blood sugar levels. If the blood sugar level is higher than normal, further testing may be done to confirm the diagnosis.
Management of Gestational Diabetes
The goal of managing gestational diabetes is to keep blood sugar levels within a target range to ensure the health of both the mother and the baby. This can be achieved through a combination of lifestyle changes and medical treatment.
A. Lifestyle Changes
Making healthy lifestyle changes can help manage gestational diabetes and reduce the risk of complications. Some of the recommended lifestyle changes include:
- Eating a healthy diet that is low in sugar and carbohydrates and high in protein and fiber
- Exercising regularly, such as walking or swimming, for at least 30 minutes a day
- Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly using a glucose meter
- Maintaining a healthy weight
B. Medical Treatment
If lifestyle changes alone are not enough to manage gestational diabetes, medical treatment may be necessary. This can include:
- Insulin injections: Insulin injections may be needed to help regulate blood sugar levels if diet and exercise alone are not enough.
- Oral medication: Some oral medications may be used to help manage blood sugar levels in women with gestational diabetes.
- Fetal monitoring: Regular fetal monitoring may be necessary to ensure the baby is growing properly and to detect any potential complications.
Complications of Gestational Diabetes
If gestational diabetes is not properly managed, it can lead to several complications for both the mother and the baby, including:
- High blood pressure
- Preeclampsia
- Premature birth
- Large birth weight
- Low blood sugar in the baby after birth
- Type 2 diabetes in the mother after delivery
Conclusion
Gestational diabetes is a common condition that affects many pregnant women in Canada. It is important for pregnant women to be screened for gestational diabetes and to manage it properly to reduce the risk of complications. By making healthy lifestyle changes and following medical treatment recommendations, women with gestational diabetes can ensure the health of both themselves and their babies.